Dropshipping has become one of the most popular ways to start an online business with minimal upfront investment. However, like any business, it requires a sound financial foundation to ensure long-term success. Building a dropshipping financial model is a critical step for anyone who wants to grow their business, secure funding, or simply make smarter business decisions. In this blog, we’ll walk through the essential steps for creating a dropshipping financial model that will help you forecast your profits, control expenses, and understand your business’s financial health. We have also built a ready-to-go Dropshipping Financial Model Template for Founders looking for an easy-to-use Financial model which will allow them to model out their financials and provide an Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement for their business.

What is a Dropshipping Financial Model?
A dropshipping financial model is a tool that helps entrepreneurs forecast the financial performance of their dropshipping business over time. By taking into account revenue projections, operating costs, and other financial metrics, a dropshipping financial model helps you understand how your business is performing and predict future outcomes. The model will cover everything from sales projections to operating costs and expected profits, providing a comprehensive view of your dropshipping operations.
For beginners, building a financial model might seem complex, but it doesn’t have to be. With a step-by-step approach, you can break down the process into manageable chunks. Let’s dive in!
Step 1: Understand the Basics of Dropshipping
Before building a financial model, it’s important to understand how dropshipping works and the key variables that will influence your financial outcomes.
In dropshipping, you sell products through your online store without ever holding inventory. When a customer makes a purchase, you forward the order to a supplier, who then ships the product directly to the customer. Your profit comes from the difference between the price at which you sell the product and the cost you pay to the supplier.
The key components of your dropshipping business that will affect your financial model include:
- Sales Revenue: The money you make from selling products.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The price you pay your supplier for each product.
- Shipping Costs: The cost of delivering the product to your customer, which may be covered by you or the supplier.
- Operating Expenses: Marketing, website maintenance, payment processing fees, and other costs related to running your store.
Step 2: Gather the Data
Before building your financial model, you need accurate data. As a new dropshipping business owner, you may not have historical data, but you can rely on industry benchmarks, research, and your business’s initial assumptions. Key data to gather includes:
2.1 Sales Data
- Average Order Value (AOV): The average amount a customer spends per order.
- Sales Volume: The number of orders you expect to process in a given period (monthly, quarterly, annually).
- Conversion Rate: The percentage of visitors to your store who make a purchase.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The amount of money you spend on marketing to acquire each customer.
2.2 Supplier and Product Data
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): The price you pay to the supplier for each product. This will vary depending on the product and the supplier.
- Shipping Fees: Some suppliers offer free shipping, while others charge a fee. Factor in these costs for each order.
- Product Pricing: The price at which you plan to sell each product in your store.
2.3 Operating Expenses
- Marketing Costs: Your budget for digital marketing campaigns (e.g., Facebook Ads, Google Ads).
- Website Costs: Monthly or annual fees for maintaining your eCommerce platform (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce) and any apps or integrations you use.
- Payment Processing Fees: The fee charged by payment processors (e.g., PayPal, Stripe) for each transaction.
- Other Operational Expenses: This could include customer service, returns management, and any other business-related costs.
Step 3: Build Your Revenue Projections
The first core part of your dropshipping financial model is projecting your revenue. To do this, you need to estimate how many sales you expect to make and at what price.
3.1 Calculate Projected Sales Volume
Start by forecasting how many sales you expect to generate each month. Use the following variables to help with your estimates:
- Website Traffic: Estimate the number of visitors to your website each month. This depends on your marketing efforts, SEO, and word of mouth.
- Conversion Rate: Use an average conversion rate for eCommerce stores, which typically ranges from 1% to 3%. For instance, if you expect 1,000 visitors to your website and have a 2% conversion rate, you would generate 20 sales.

3.2 Calculate Revenue per Sale
Multiply the number of sales by the price at which you plan to sell each product. This will give you your total revenue.

Example:
Let’s say your average order value (AOV) is $50, and you expect to make 200 sales per month.
- Revenue = 200 sales × $50 = $10,000 in monthly revenue.
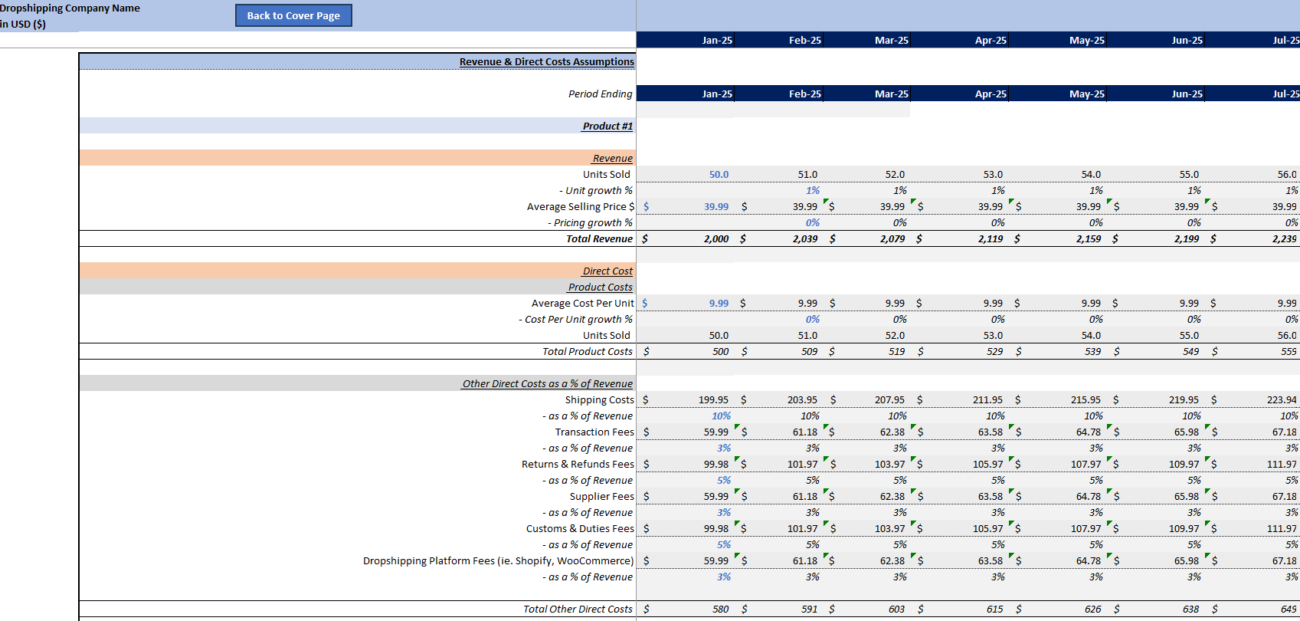
Step 4: Estimate Your Costs (COGS and Operating Expenses)
The next step in your financial model is estimating your costs. This will help you understand how much money you’ll need to spend to make your business run and how much profit you can expect.
4.1 Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
For each sale, you’ll pay your supplier a certain amount for the product. Multiply your sales volume by the COGS to get your total costs for the month.

4.2 Shipping Costs
Shipping costs can vary depending on your supplier and the destination of the order. If you’re covering shipping costs, factor them into your overall expense calculations.

4.3 Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are the fixed and variable costs required to keep your business running. These may include:
- Marketing and Advertising: Budget for Google Ads, Facebook Ads, Instagram promotions, etc.
- Website and Platform Fees: Monthly fees for eCommerce platforms like Shopify or WooCommerce.
- Payment Processing Fees: Fees charged by PayPal or Stripe for each transaction (usually 2.9% + $0.30 per transaction).
- Other Expenses: Costs like apps, email marketing services, or customer support tools.
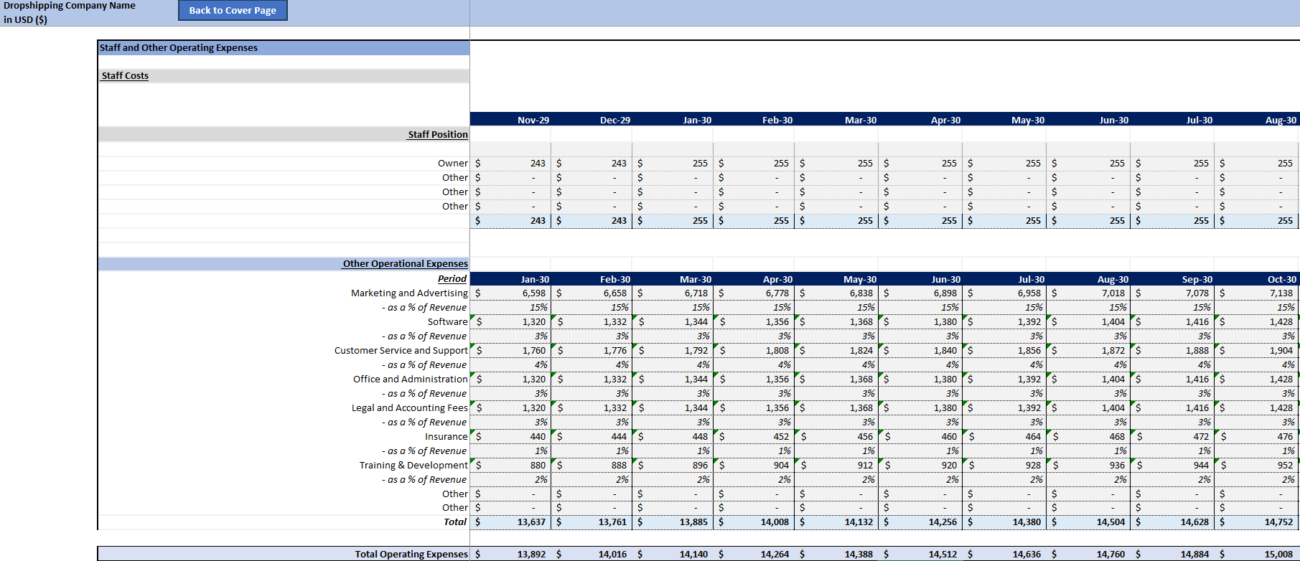
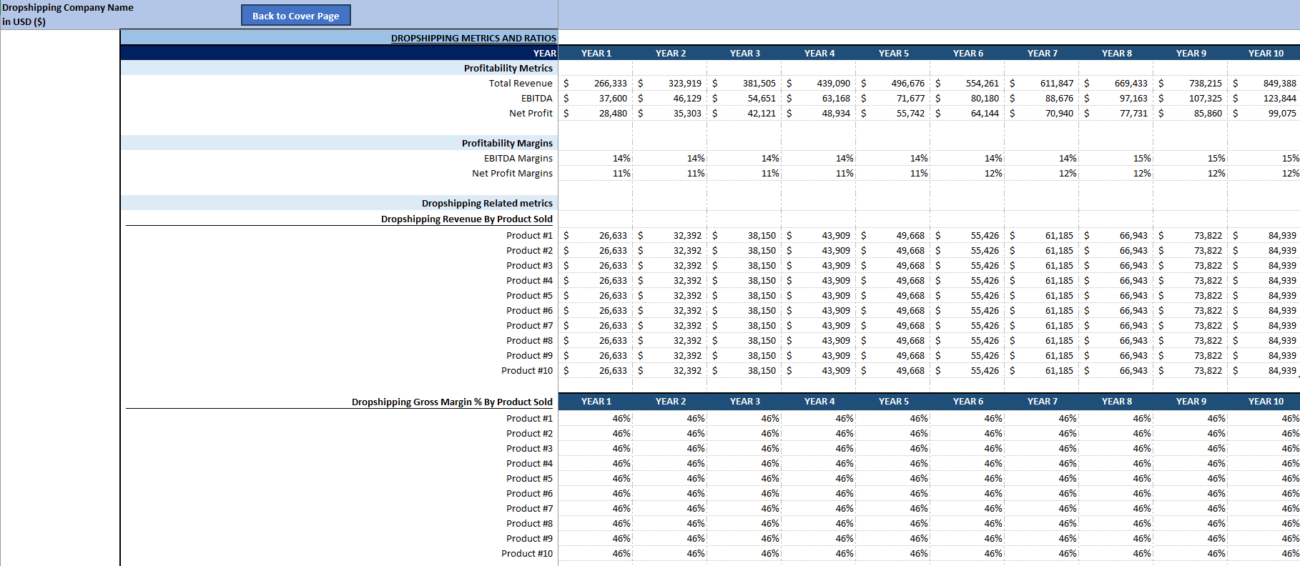
Step 5: Build Your Income Statement
The income statement is one of the most important parts of your financial model. It shows your revenue and expenses, allowing you to calculate your net profit.
5.1 Revenue
Start by listing your total revenue, which you calculated earlier.
5.2 Costs and Expenses
List out your total costs for the month, including:
- COGS
- Shipping costs
- Operating expenses (marketing, platform fees, etc.)
5.3 Calculate Gross Profit
Your gross profit is the revenue remaining after subtracting the cost of goods sold and shipping costs:
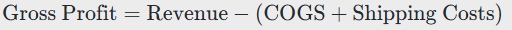
5.4 Calculate Net Profit
To calculate your net profit, subtract your operating expenses from your gross profit:

Step 6: Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement is an essential component of your financial model. This will help you manage your cash flow and ensure that you have enough liquidity to cover your expenses.
6.1 Cash Inflows
Your main cash inflow comes from the payments made by customers. Add these up for each month.
6.2 Cash Outflows
Cash outflows will include your supplier payments (for COGS), shipping fees, marketing costs, and any other operational expenses.
6.3 Net Cash Flow
Calculate your net cash flow by subtracting your outflows from your inflows:

This will show whether you’re generating enough cash to keep your business running or if you need additional funding.
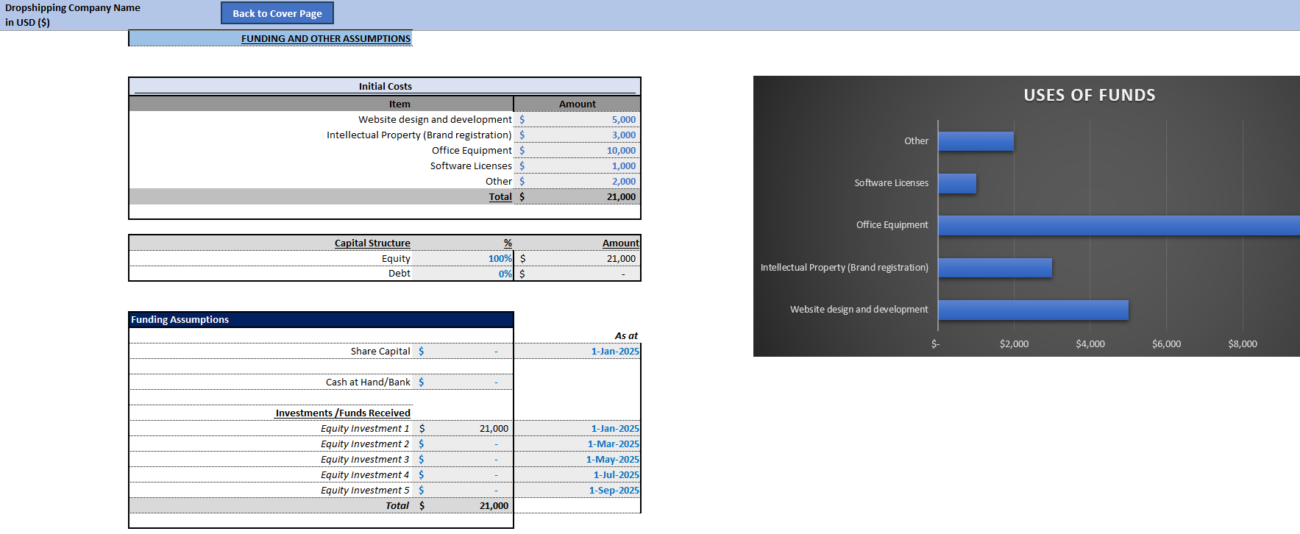
Step 7: Break-Even Analysis
A break-even analysis helps you understand when your dropshipping business will start becoming profitable. It shows how much revenue you need to cover your fixed costs. To calculate your break-even point, divide your fixed costs by your contribution margin (which is your revenue per sale minus your variable costs per sale):

This will give you the number of sales needed to cover your fixed costs.
Step 8: Monitor and Adjust Your Model
Building the financial model is just the first step. As you grow your business, regularly monitor your performance against the projections. Make adjustments to your assumptions based on real data to improve the accuracy of your model.
Final Thoughts!
Building a dropshipping financial model is an essential step for any entrepreneur who wants to grow their business with confidence. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create a model that allows you to forecast your revenue, manage your costs, and understand the financial health of your business. With a solid financial foundation, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions, scale your operations, and ultimately achieve success in the competitive world of dropshipping.

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a financial model template?
A financial model template is a pre-built structure that helps dropshipping business owners create detailed financial projections. Templates can be easily customized to fit specific business needs.
2. How do cash flow statements help in financial management?
Cash flow statements provide insights into the cash inflows and outflows of your business. They are crucial for maintaining liquidity and ensuring that you have enough cash to cover your operational expenses.
3. What role does a third-party supplier play in dropshipping?
A third-party supplier in dropshipping is responsible for inventory and shipping products directly to customers. They allow business owners to run their stores without holding any physical stock.



