Running a farm effectively involves much more than just tending to crops or livestock—it requires a deep understanding of financial management. A solid farm financial model is essential, whether you’re operating a small family farm or a large commercial enterprise. It helps you track expenses, forecast revenues, and plan for sustainable growth. We have also built a ready-to-go Farm Financial Model Template for owners looking for an easy-to-use Financial model which will allow them to model out their farm financials and provide an Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement for their farm.

What is a Farm Financial Model?
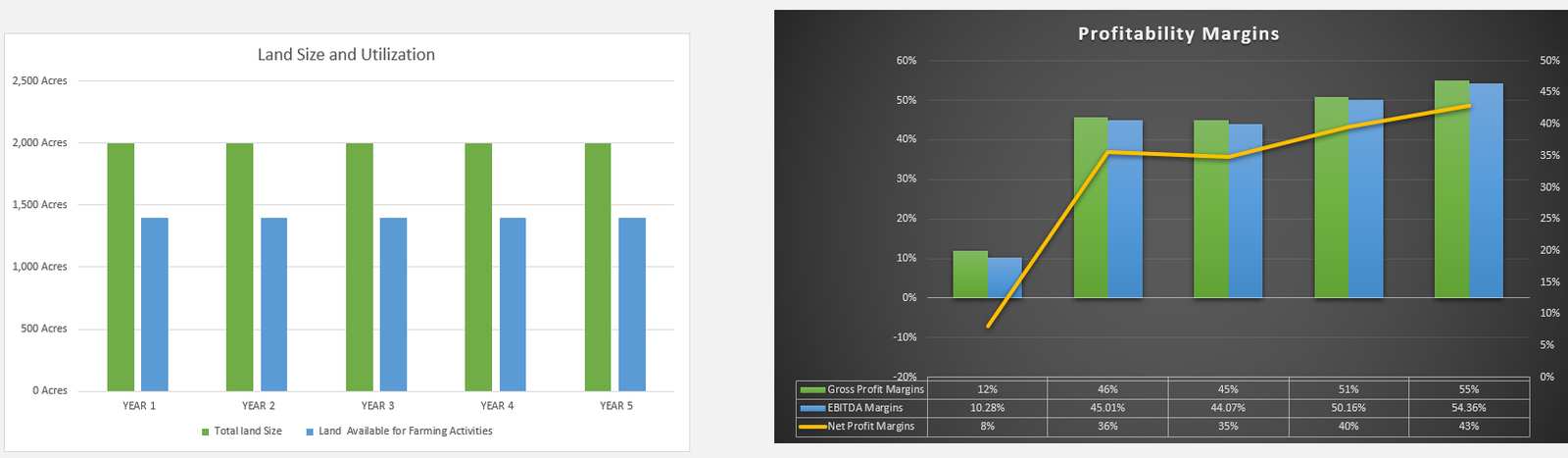
A farm financial model is a structured tool designed to forecast the financial performance of your farm. It covers various assumptions about income, expenses, and investments, helping you manage cash flow and make data-driven decisions. Learn more about developing a farm financial model.
Key Components
- Revenue Forecast: Income expectations from farming activities.
- Operating Expenses: Costs such as labor, equipment, and feed.
- Capital Expenditures (CapEx): Long-term investments like equipment.
- Cash Flow: Movement of money in and out of the business.
- Profit and Loss (P&L) Statement: Summary of revenues, costs, and profits.
- Balance Sheet: Snapshot of financial position, detailing assets and liabilities.
Step 1: Data Collection and Setting Assumptions
Gather all relevant data and set realistic assumptions. Historical financial info is invaluable, as is research on industry benchmarks for different types of farming. Use resources like this PDF guide on developing a farm financial model for additional insights.
Essential Data
- Past Financial Data: Analyze past income, costs, and investments.
- Industry Benchmarks: Research costs, revenues, and yields.
- Growth and Pricing Assumptions: Predict growth and set product prices by considering market trends and seasonal fluctuations.
Step 2: Forecasting Revenues
Revenue forecasting is crucial and typically comes from selling farm products. Consider both production volumes and pricing, following insights from agriculture project finance models.
Steps for Estimation
- Estimate Production Volume: Consider acreage for crops and livestock numbers.
- Price Your Products: Research market prices and factor in variability.
- Calculate Revenue: Multiply expected production by unit price.
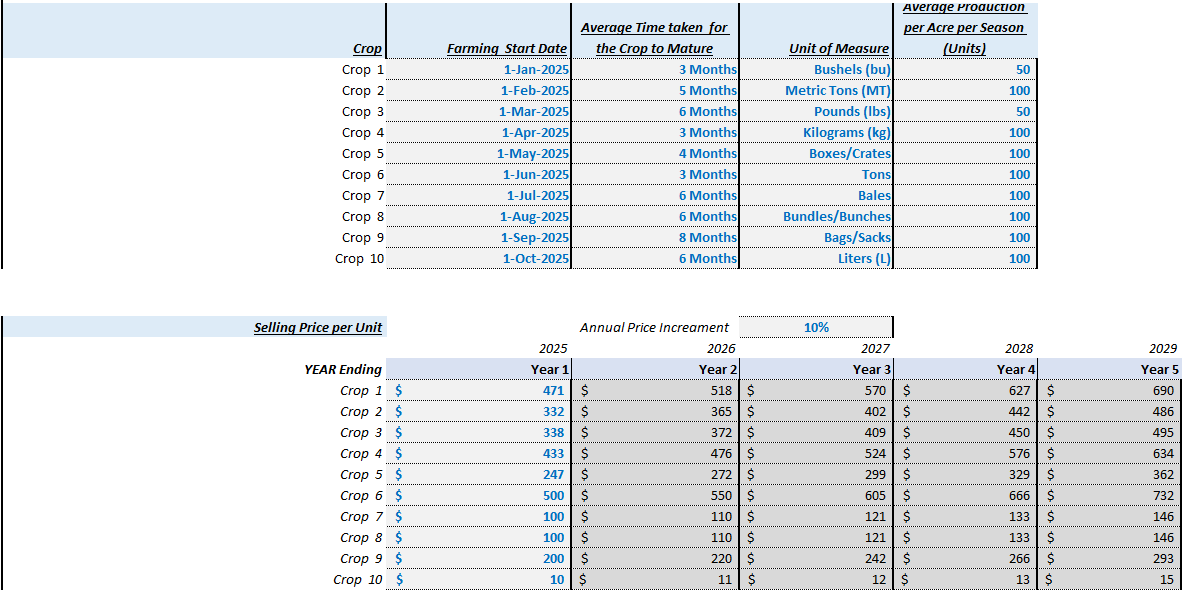
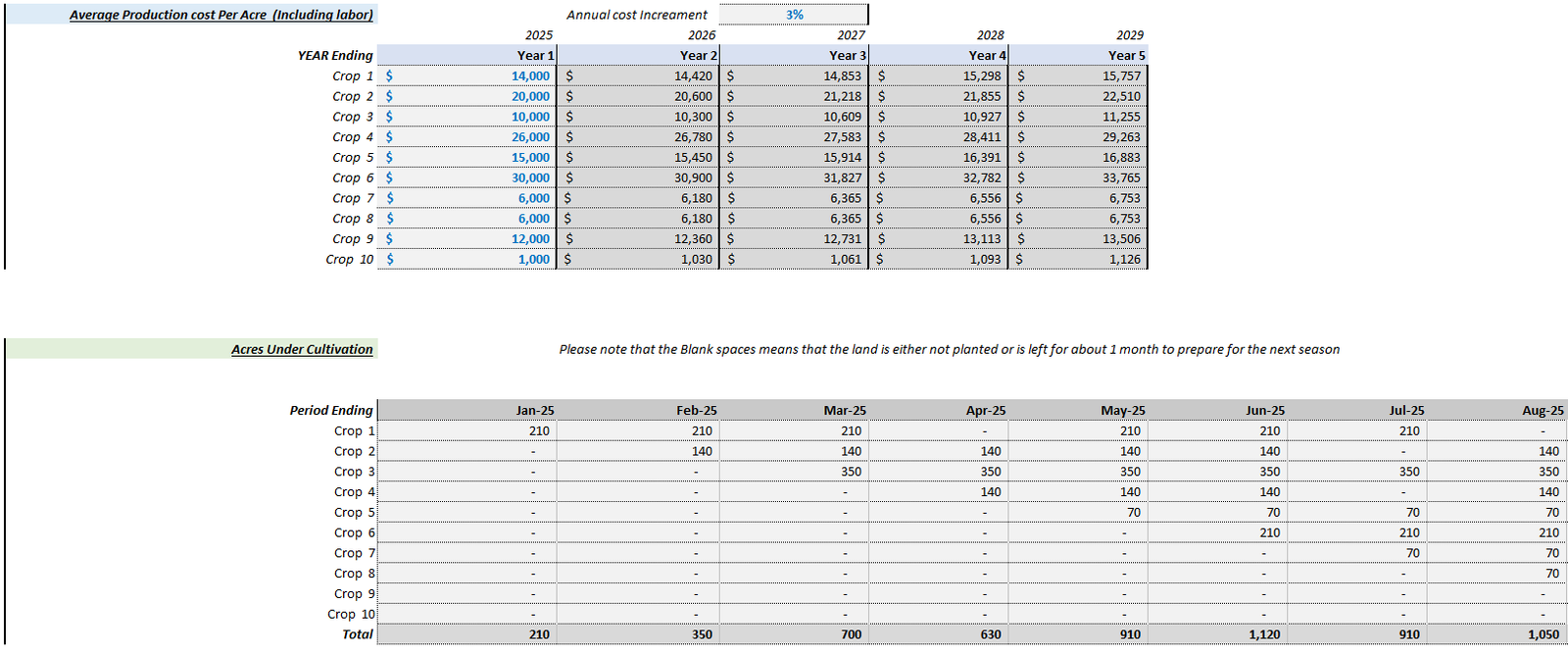
Step 3: Estimating Costs and Expenses
Project the costs involved in running the farm, categorizing them as variable (direct) and fixed (operating) costs. Identify CapEx requirements as well, using examples like those in farm development models.
Cost Categories
- Variable Costs: Include seeds, feed, and labor.
- Fixed Costs: Include rent, insurance, and utilities.
- CapEx: Major investments in equipment and infrastructure.
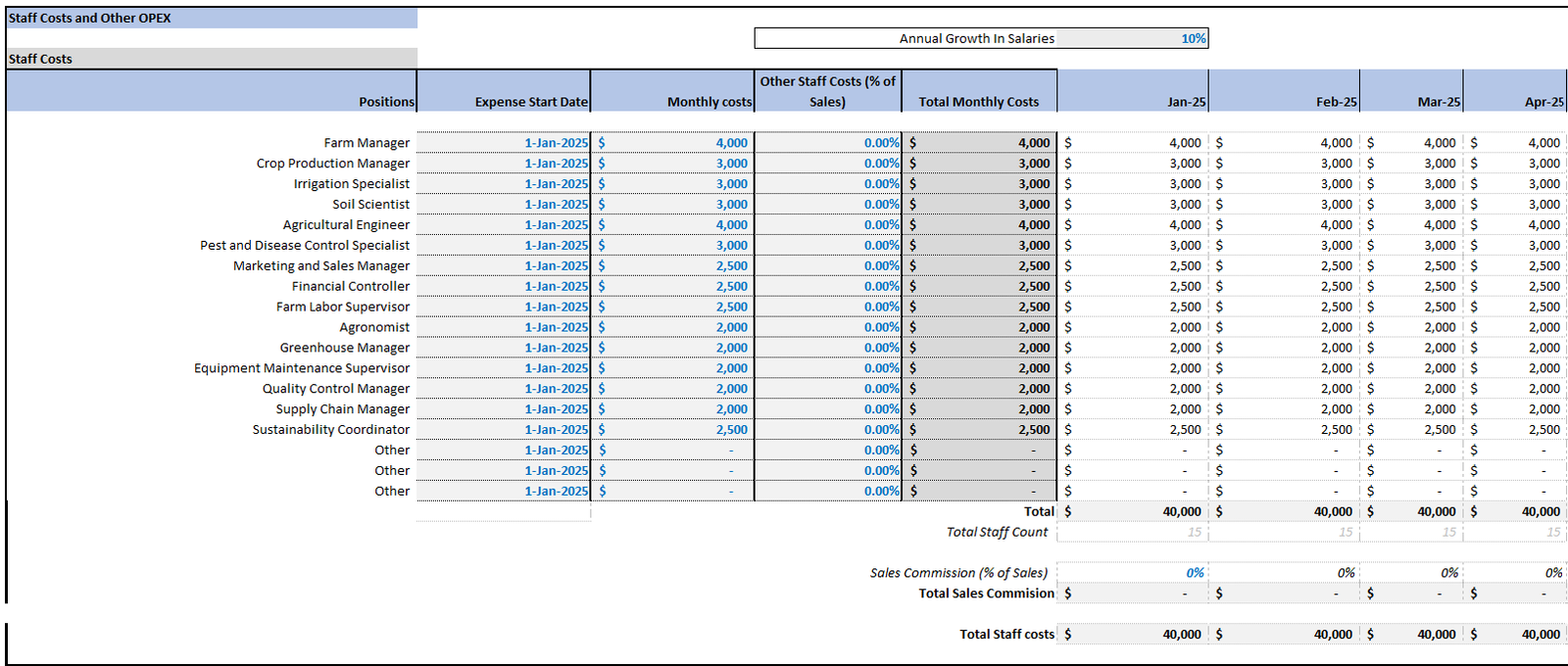
Step 4: Building Financial Statements
Compile your estimations into main financial statements: P&L statement, cash flow statement, and balance sheet. These reflect the farm’s financial health comprehensively. Additional resources can be found in this farm financial model example.
Key Elements
- P&L Statement: Summarizes revenues and expenses.
- Cash Flow Statement: Tracks cash movement.
- Balance Sheet: Shows assets, liabilities, and equity.
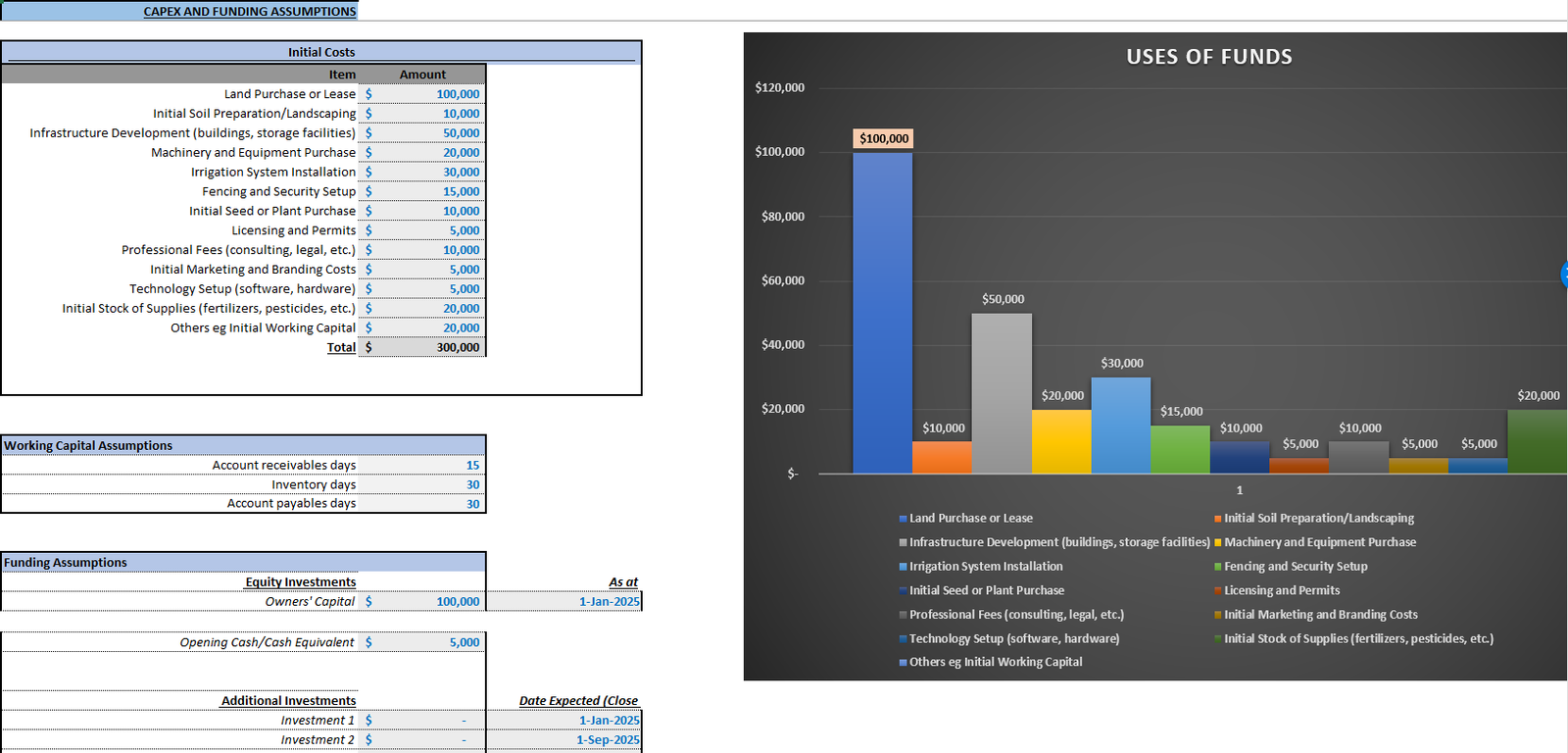
Step 5: Regular Review and Adjustment
Regularly reviewing and adjusting your financial model is crucial. Farms face fluctuating conditions and market demands, requiring flexibility and proactive management. Resources like financial modeling in Excel can aid in ongoing analysis.
Final Thoughts!
Effective farm business management hinges on a robust financial model, guiding farms towards profitability and growth. By continuously refining your model with current data and industry insights, you’ll be well-prepared to navigate financial challenges and capitalize on opportunities, ensuring long-term sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main components of a farm financial model?
Key components include revenue forecasts, operating expenses, CapEx, cash flow analysis, and financial statements.
Why is a financial model important for farming?
It helps track expenses, predict revenues, and make informed decisions, crucial for long-term success.
How often should I update my farm financial model?
Frequently—ideally quarterly or semi-annually—to adapt to changes in market conditions and farm operations.
This structured approach not only enhances farm development analysis but also supports agriculture business finance and underwriting farm investments, aligning with optimal financial outcomes.



