Starting a gym can be a rewarding venture, offering a chance to help people achieve their fitness goals while also building a profitable business. However, starting a gym requires careful planning and strategy, particularly when it comes to financials. A well-constructed financial model helps you understand the financial viability of your gym, manage cash flow, secure funding, and set realistic growth targets.
This guide will walk you through the process of building a gym financial model from scratch, step by step, with tips and advice tailored for beginners. We have also built a ready-to-go Startup Gym Financial Model Template for Founders looking for an easy-to-use Financial model which will allow them to model out their gym financials and provide an Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement for their gym.

What is a Financial Model for a Gym?
A financial model is a tool used by businesses to represent their financial performance over time. It typically consists of spreadsheets detailing revenue, costs, investments, and profitability. For a gym startup, a financial model is crucial to ensuring profitability and sustainability. Learn more about building a gym financial model from resources like SharpSheets.
Why is a Financial Model Important for Your Gym?
A financial model is important for several reasons:
- Cash Flow Management: It helps forecast income and expenses, ensuring that the gym can cover operational costs such as salaries and utilities.
- Fundraising: A detailed financial model is essential when presenting to investors or lenders, demonstrating a viable path to profitability.
- Business Decisions: It allows data-driven decisions on pricing, membership fees, and services.
- Sustainability: Ensures long-term viability by considering growth rates and external challenges.
Explore more about creating financial projections from Glofox.
Step 1: Define Your Gym’s Business Model
Understand your gym’s business model before delving into financials. Below are common business models:
- Membership-Based Model: Members pay a periodic fee for access.
- Pay-Per-Use Model: Customers pay per visit or class.
- Hybrid Model: Combines memberships and pay-per-use services.
Determining your business model will guide how you estimate revenue.
Step 2: Forecast Revenue Streams
Identifying multiple revenue streams is crucial for realistic projections.
Membership Fees
Membership fees are typically the main revenue source. Estimate the member count, fee average, and retention rate.
Example:
- Expected members: 300
- Average fee: $50/month
- Annual revenue: 300 × $50 × 12 = $180,000
Personal Training
Personal training is a high-margin service. Revenue depends on session count and price.
Example:
- Sessions/month: 200
- Price/session: $40
- Annual revenue: 200 × $40 × 12 = $96,000
Group Classes
Offering classes like yoga or spinning either included in membership or sold separately.
Example:
- Classes/week: 10
- Attendance/class: 15
- Price/class: $10
- Annual revenue: 10 × 15 × $10 × 52 = $78,000
Retail and Merchandise
Selling gear and supplements can be another revenue stream.
Example:
- Sales/member: $5/month
- Annual revenue: 300 × $5 × 12 = $18,000
Additional Services
Consider additional services such as massage therapy to boost revenue.

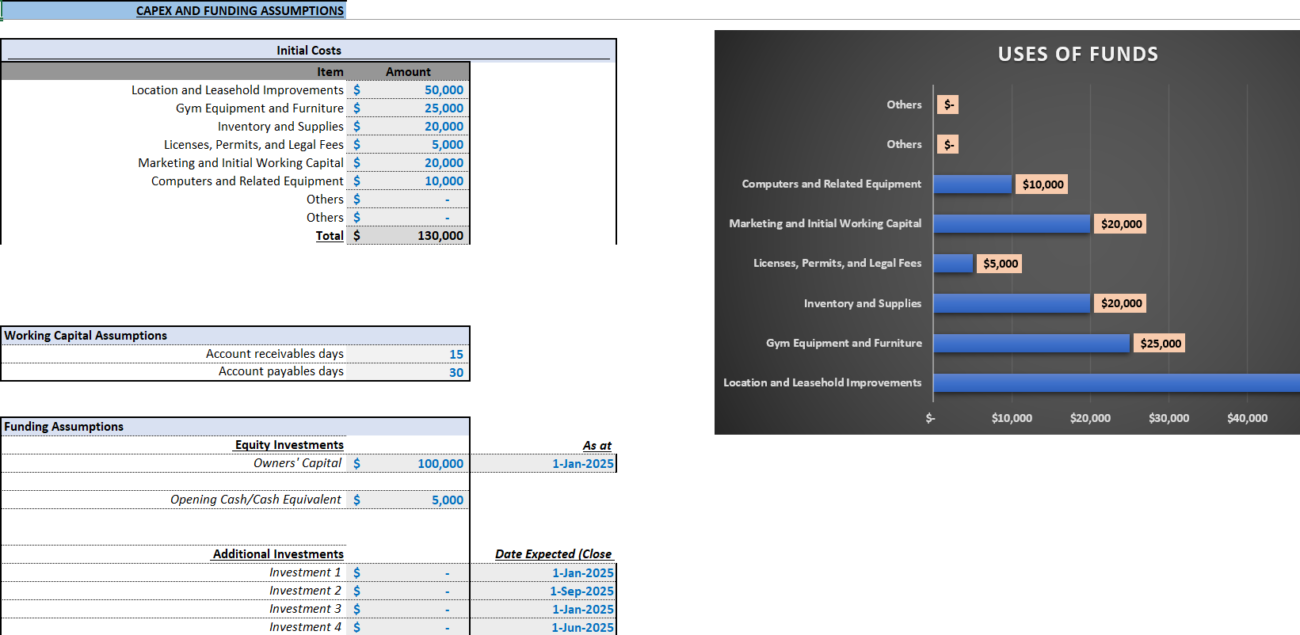
Step 3: Estimate Your Startup Costs
Understanding your revenue helps to pinpoint initial expenses.
Equipment Costs
Buying or leasing equipment is a significant startup expense.
Example:
- Treadmills: $5,000 each × 3 = $15,000
- Weight machines: $2,000 each × 5 = $10,000
- Total equipment cost: $30,000
Lease and Facility Costs
Lease or mortgage costs vary by location and space size.
Example:
- Monthly rent: $5,000
- Annual rent: $60,000
Staff Salaries
Estimate salaries for trainers and support staff.
Example:
- Manager salary: $50,000
- Total salaries: $180,000
Explore more about gym budgeting from Eloquens.
Marketing and Advertising
Include both online and offline strategies in your budget.
Example:
- Initial campaign: $10,000
- Annual expenses: $22,000
Legal, Licensing, and Insurance
Account for fees that ensure legal compliance.
Example:
- Legal and insurance fees: $5,000
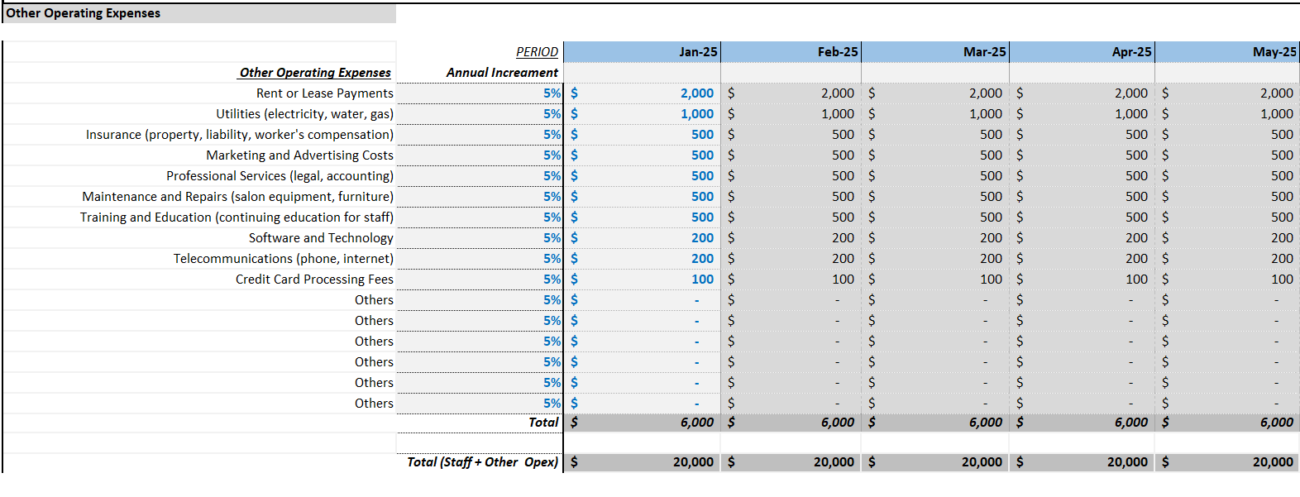
Step 4: Calculate Operating Expenses
Ongoing costs are crucial for day-to-day operations.
Example:
- Utilities: $2,000/month
- Supplies & Maintenance: $1,000/month
- Annual operating expenses: $36,000

Step 5: Build Your Financial Statements
Using revenue, costs, and expenses to create:
- Income Statement: Shows revenue, costs, and profits.
- Cash Flow Statement: Tracks cash movement to ensure liquidity.
- Balance Sheet: Lists assets, liabilities, and equity.
Step 6: Project Future Growth
Estimate growth in revenue, membership, and expenses over the next 3–5 years for strategic decisions.
Learn more from Upmetrics.

Final Thoughts!
Building a financial model for your gym ensures its success and sustainability. It provides a roadmap for financial success by understanding revenues, estimating costs, and forecasting growth. Regularly review and update your financial model to adapt to changing market conditions.
FAQ
What are the main components of a gym financial model?
A gym financial model includes income statements, cash flow statements, and balance sheets, forecasting revenue streams, costs, and expenses.
Why do I need a financial model for my gym?
A financial model is essential for cash flow management, fundraising, strategic decisions, and ensuring long-term sustainability.
How can I forecast gym revenue accurately?
Forecast revenue accurately by analyzing membership fees, personal training, group classes, retail sales, and additional services.
Access advanced Excel templates for gym startups at SmartHelping. With a robust financial model, you can make informed decisions, attract investors, and grow your gym into a thriving business.



