Building a successful subscription-based SaaS (Software as a Service) business can be incredibly rewarding, offering the potential for recurring revenue and scalable growth. To succeed in this competitive market, you need more than just a great product—you need a solid financial model to guide your strategy and ensure your business is financially viable.
This article will walk you through the process of building a subscription-based B2C SaaS financial model step-by-step. We’ll cover everything from estimating startup costs to projecting revenue, understanding key metrics like Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Lifetime Value (LTV), and forecasting cash flow. By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive financial model that helps you understand your SaaS business’s financial health and make data-driven decisions.
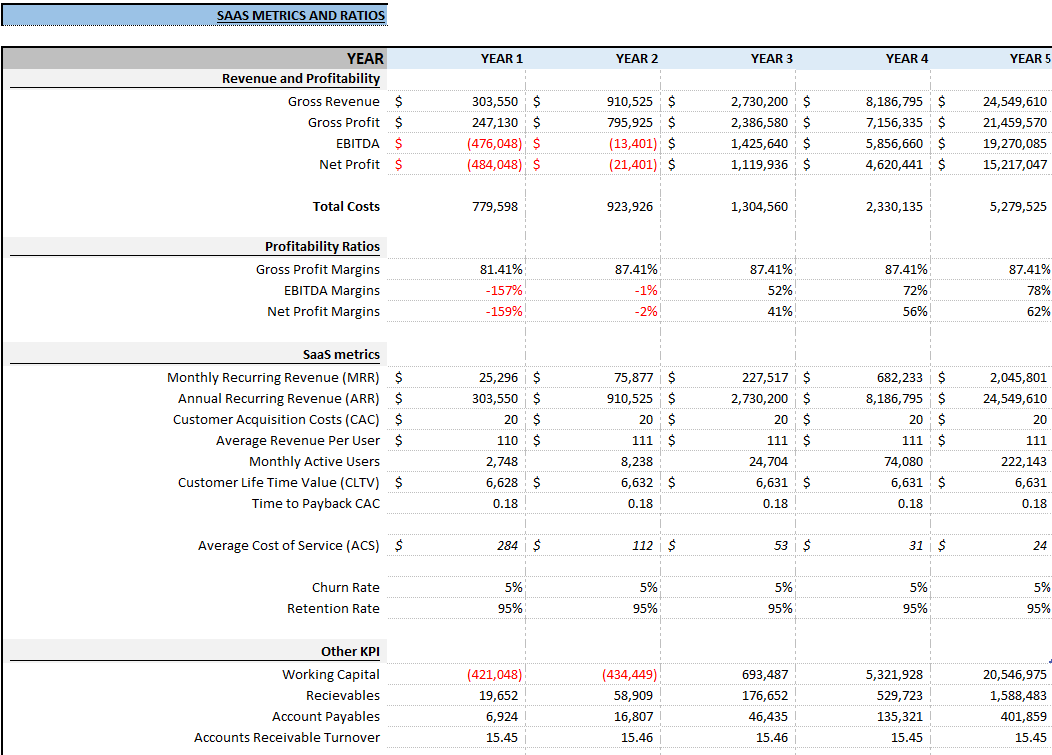
We have also built a Subscription-Based B2C SaaS Financial Model Template for Founders and Entrepreneurs to use. Just input your assumptions, and our model does the rest! It’s a complete 3-way financial model with an Income Statement, Balance Sheet, Cash Flow Statement, SaaS specific metrics, ratios, and more.

Understanding the Basics of a Subscription-Based B2C SaaS Financial Model
A financial model for a subscription-based SaaS business helps predict the financial performance of your company. It incorporates several key elements, including revenue, costs, customer metrics, and cash flow, to give you a comprehensive view of how your business is performing and what its future may look like.
In the case of a B2C (business-to-consumer) SaaS business, your customers are individual consumers. As a result, your financial model will need to account for:
- Recurring Revenue: Subscription-based revenue is the backbone of your SaaS business model. Understanding how it will grow over time is crucial.
- Churn Rate: The rate at which customers cancel their subscriptions.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The cost of acquiring a new customer.
- Lifetime Value (LTV): The total revenue you expect to generate from a customer over their entire relationship with your company.
Key components of a B2C SaaS financial model include:
- Startup Costs: One-time expenses incurred in launching the product.
- Operating Expenses: Ongoing costs of running the business, including salaries, marketing, and technology.
- Revenue Projections: Subscription fees, potential upsell opportunities, and additional product offerings.
- Cash Flow Projections: Estimating how much cash will flow in and out of your business, considering both revenue and expenses.
Building a robust financial model allows you to set achievable goals, assess the health of your business, and make strategic decisions about funding, scaling, and pricing.
Step 1: Estimate Your Initial Startup Costs
The first step in building your financial model is estimating the initial costs to get your B2C SaaS business off the ground. These startup costs typically include product development, technology infrastructure, and the necessary resources to launch the business.
Product Development Costs
Developing a SaaS product involves both front-end (what users see) and back-end (the infrastructure behind the scenes) development. Initial costs here could include:
- Development Team: Costs associated with hiring developers, designers, and product managers to create the software. You can choose to build your financial model from scratch or outsource development.
- Tech Stack: Investments in cloud hosting, APIs, third-party tools, or other technologies necessary for the app’s functionality.
- Beta Testing and QA: Expenses related to ensuring the software works as expected and fixing bugs.
- Software Licenses: Consider licensing fees for any paid tools, software, or platforms required to build your product.
Marketing and Branding Costs
Even before you launch your product, you need to start marketing it to build awareness. Key expenses in this area include:
- Website Development: Building a professional website that explains your product and captures leads. You can utilize platforms that offer templates, such as the B2C SaaS Financial Model & Valuation Template.
- Branding: Logo design, branding materials, and other creative assets.
- Pre-launch Campaigns: Costs for email marketing, paid ads, or influencer partnerships to generate buzz.
Legal and Administrative Costs
Ensure your business is legally protected and compliant. This includes:
- Business Incorporation: Fees for setting up your business as a legal entity (LLC, corporation, etc.).
- Legal Fees: For drafting contracts, terms of service, privacy policies, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Accounting Setup: Initial accounting software setup or hiring accountants.
Operating Expenses Setup
To get started, set aside funds for initial operating expenses such as:
- Office Space (if applicable): Rent, utilities, and office supplies if you’re not operating remotely.
- Equipment: Computers, software tools, and other technology required for day-to-day operations.

Step 2: Estimate Your Ongoing Operating Expenses
Once your SaaS business is up and running, you’ll face ongoing expenses. These are recurring costs that need to be factored into your financial model. Common operating expenses for a subscription-based B2C SaaS business include:
Personnel Costs
Your team will likely be the largest ongoing expense. This can include:
- Salaries: Payments for full-time or part-time employees, including developers, customer support, sales, and marketing staff.
- Freelancers/Contractors: Costs for outsourcing specific roles, such as designers or copywriters.
- Benefits: Health insurance, retirement plans, and other employee perks.
Hosting and Technology Costs
Your SaaS business will rely on cloud hosting, APIs, and other technology tools to run smoothly. Key costs include:
- Cloud Hosting: Monthly or annual fees for hosting your software on platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure.
- Third-party Software: Subscriptions to tools and platforms that complement your SaaS product.
- Security and Compliance: Expenses related to ensuring your product is secure and compliant with data regulations.
Marketing and Customer Acquisition Costs
In a B2C SaaS model, customer acquisition is vital to growth. Common marketing and sales expenses include:
- Digital Marketing: Advertising through channels like Google Ads, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, etc.
- Content Marketing: Creating blog posts, videos, and other content to attract and engage potential customers, as highlighted in this introductory guide.
- Email Campaigns: Subscriptions to email marketing services.
- Sales Team: Salaries and commissions for salespeople who help close deals.
- Customer Retention: Budgeting for loyalty programs, email newsletters, and other methods to retain customers.
Customer Support and Service Costs
Providing excellent customer service is critical for a subscription-based business, and this comes with associated costs:
- Support Team Salaries: Customer support staff responsible for resolving user issues.
- Software for Support: Subscription to tools like Zendesk or Intercom to manage customer inquiries.
General and Administrative Costs
These are overhead expenses that ensure your business continues running smoothly:
- Accounting and Legal Services: Fees for accountants and lawyers to ensure tax compliance and handle contracts.
- Office Supplies: Costs of supplies like paper, coffee, and other necessities.
- Insurance: General business insurance, liability coverage, etc.
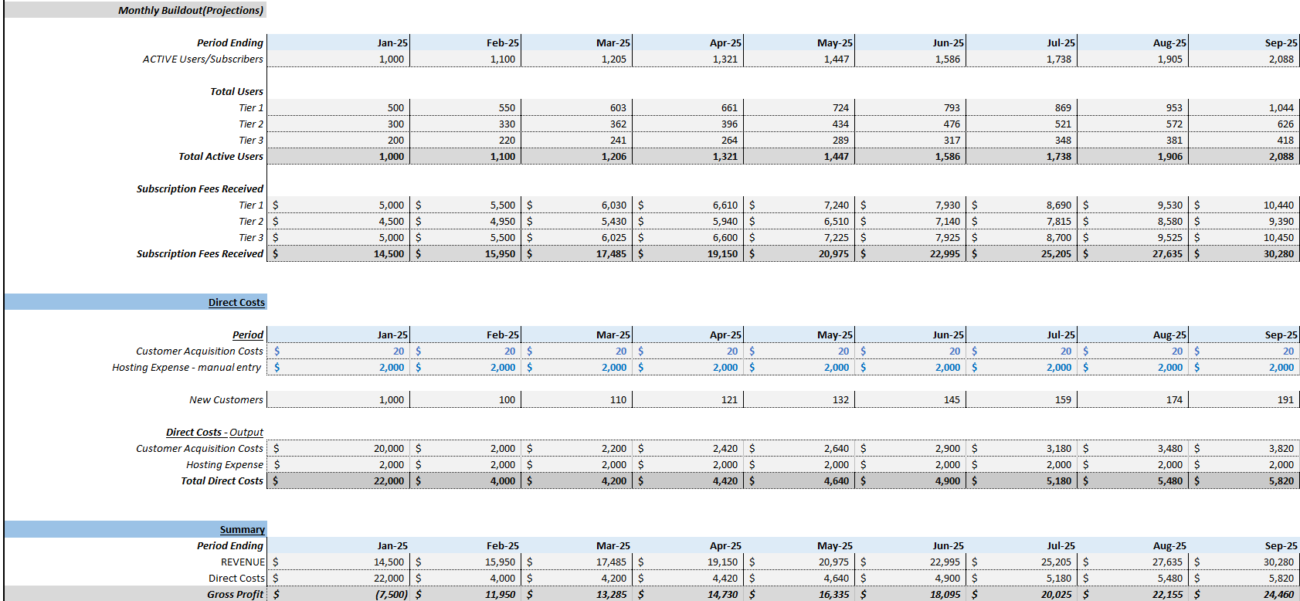
Step 3: Estimate Your Revenue
Revenue in a B2C SaaS business is typically generated through subscription fees. It’s important to forecast both the number of customers expected and the pricing strategy adopted. Key elements of revenue projection include:
Pricing Strategy
Your pricing model will determine how much revenue you generate per customer. Some common SaaS pricing models for B2C businesses include:
- Flat-Rate Pricing: One fixed price for all customers, regardless of usage.
- Tiered Pricing: Different pricing tiers based on usage or features.
- Freemium: A free version of the software with the option to upgrade to a paid version with additional features.
- Pay-Per-Use: Charging customers based on how much they use the service.
Consult resources like the B2C and B2B SaaS Financial Model Template to determine your pricing strategy.
Customer Growth
To project revenue, forecast customer growth. Key metrics include:
- Customer Acquisition Rate: How many new customers you expect to acquire each month or quarter.
- Customer Churn Rate: The percentage of customers who cancel their subscriptions each month. A lower churn rate means higher customer retention.
- Average Revenue Per User (ARPU): The average amount of revenue earned from each customer per month or year.
Additional Revenue Streams
If applicable, consider other ways to generate revenue:
- Upsells: Additional products or services that complement the core offering.
- Affiliate Marketing: Earnings from referring customers to third-party services.
- Ad Revenue: Generate income through advertising if offering a free version of the software.
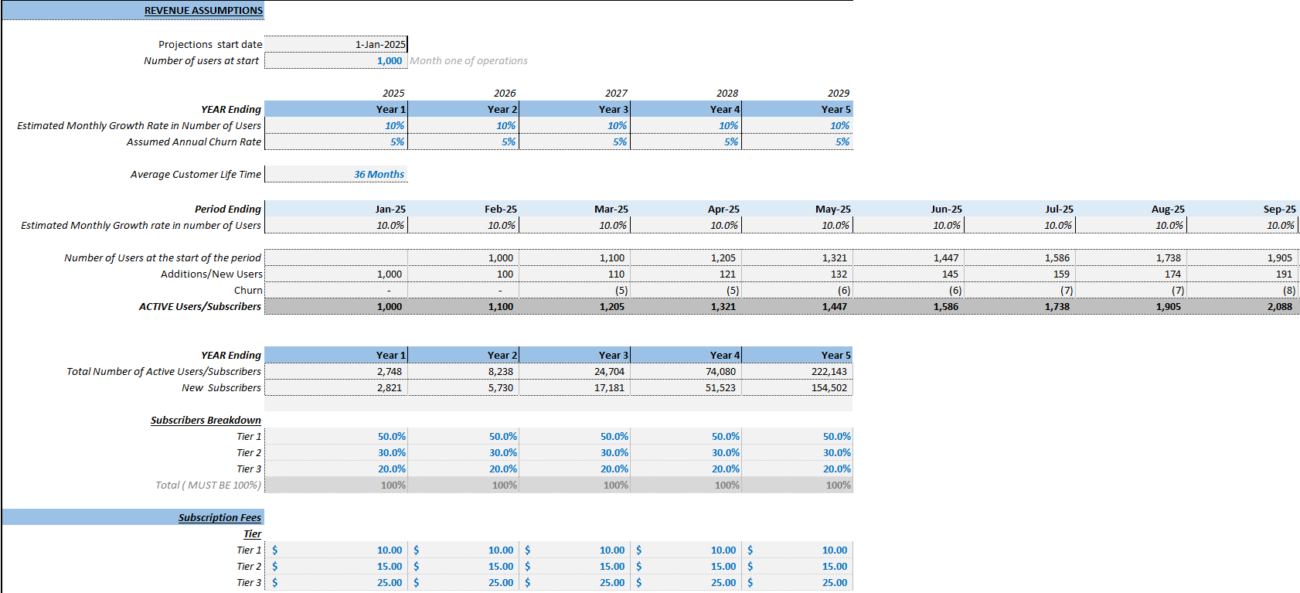
Step 4: Key Metrics to Include in Your Financial Model
The success of a B2C SaaS business can be determined by tracking key metrics that directly influence financial performance. Here are some essential metrics to include:
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
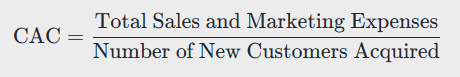
Lifetime Value (LTV)
LTV measures how much revenue you expect to earn from a customer over their lifetime with your company. This is essential to understanding the value of a customer and how much can be spent on acquiring new ones. Calculate LTV as:
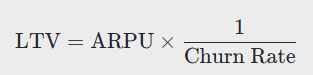
Churn Rate
Churn is the percentage of customers who cancel their subscription during a given time period. High churn rates negatively affect growth, so it’s essential to minimize it.
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
MRR represents the predictable revenue expected from subscriptions each month:

Step 5: Project Cash Flow and Profitability
Estimate revenue, costs, and key metrics to project cash flow and profitability. This involves:
- Monthly Cash Flow Projections: Forecasting how much cash will come in and go out each month.
- Breakeven Analysis: Determining when your business will become profitable, i.e., when your revenue exceeds expenses.
Conclusion
Building a financial model for your subscription-based B2C SaaS business is essential for understanding how your company will perform financially and whether it is sustainable in the long term. By estimating startup costs, ongoing expenses, and revenue projections, you can create a comprehensive financial roadmap to guide decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a subscription revenue model?
A subscription revenue model is a business model where customers pay a recurring fee to access a product or service, rather than a one-time purchase. This model is often preferred for its potential to generate stable, predictable income over time.
How do I calculate the Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)?
CAC is calculated by dividing the total sales and marketing expenses by the number of new customers acquired over a specific period. This metric is critical for understanding how efficiently your marketing efforts are converting prospects into paying customers.
What is the importance of lifetime value (LTV) in a SaaS financial model?
LTV is important because it estimates the total revenue you expect from a customer over their relationship with your company. This helps determine how much can be invested in acquiring new customers and informs pricing and marketing strategies.
Optimize your subscription-based B2C SaaS startup by creating a detailed financial model tailored to your unique business needs.



