The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries are renowned for their innovation, breakthroughs, and the critical role they play in improving public health. However, these industries are also fraught with high levels of uncertainty and risk. From the unpredictability of drug development timelines to regulatory hurdles, market competition, and pricing pressures, navigating financial risk is an essential aspect of ensuring long-term success in pharma and biotech ventures.
Given the complexity of these risks, having a robust financial model is crucial. Financial modeling in the pharma and biotech sectors is not only a tool for managing cash flows and profitability but also a strategic framework for making informed decisions, securing funding, and planning for various market scenarios. In this article, we will explore how pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies can leverage financial modeling strategies to navigate the inherent risks and uncertainties of their industries. We have also built a ready-to-go Pharma and Biotech Valuation and Financial Model Template for Founders looking for an easy-to-use Financial model which will allow them to model out their company’s financials and provide an Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement for their company.

Understanding the Unique Risks in Pharma and Biotech
Before diving into financial modeling strategies, it’s essential to understand the types of risks that pharma and biotech companies face:
Research and Development (R&D) Risk
Drug development is a lengthy, expensive, and uncertain process. The success rate of developing a new drug is low, with only a small percentage of drugs in development ultimately receiving FDA approval. The cost of R&D is high, and clinical trials—critical steps in the development process—carry the risk of failure at any stage, leading to substantial financial losses.
Regulatory Risk
Pharmaceutical and biotech companies must navigate complex regulatory requirements to bring a drug to market. Regulatory approval processes are often time-consuming and expensive, with the risk of delays or denials. Changes in regulatory standards can also impact the speed and cost of drug development.
Market and Commercialization Risk
Even after successful clinical trials and regulatory approval, there is no guarantee that a product will succeed commercially. Market competition, pricing pressures, and the uncertainty of market adoption all pose significant risks. Additionally, unforeseen challenges, such as patent expirations or generic competition, can quickly erode profitability.
Operational and Supply Chain Risk
Pharma and biotech companies rely heavily on complex supply chains for raw materials, manufacturing, and distribution. Any disruption—whether due to geopolitical events, natural disasters, or supply chain bottlenecks—can negatively impact production timelines and costs.
Intellectual Property (IP) Risk
Intellectual property is a core asset for pharmaceutical and biotech companies. However, IP can be threatened by patent expirations, patent infringement lawsuits, or challenges from generic drug manufacturers. The uncertainty surrounding IP rights and enforcement can significantly affect future revenue projections.
The Role of Financial Modeling in Risk Management
Financial modeling serves as a powerful tool to manage and mitigate risks in the pharma and biotech industries. A well-constructed financial model helps businesses project future performance, assess the viability of different scenarios, and make data-driven decisions in the face of uncertainty.
Key functions of financial modeling include:
- Cash Flow Forecasting: The ability to forecast cash inflows and outflows is crucial, especially when drug development takes years and significant capital investments are required before generating revenue. Financial models help determine how long a company can sustain operations before reaching the breakeven point.
- Scenario Analysis: Given the high level of uncertainty, companies in the pharma and biotech sectors benefit from creating multiple scenarios in their financial models. These scenarios—ranging from best-case to worst-case—help companies understand the potential outcomes and prepare for the unexpected. For more insights on scenario analysis, explore the Spinnaker post which discusses its strategic edge.
- Valuation: Financial models are used to value companies, products, and projects. Valuation methods like discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis help stakeholders estimate the value of a company based on its projected cash flows, taking into account risk factors such as R&D costs, regulatory timelines, and market adoption rates.
- Fundraising: For biotech and pharmaceutical companies, securing funding—whether from venture capital, private equity, or public markets—is often essential to fund R&D efforts. A strong financial model helps communicate the company’s potential, justify investment needs, and attract investors by showcasing potential returns.
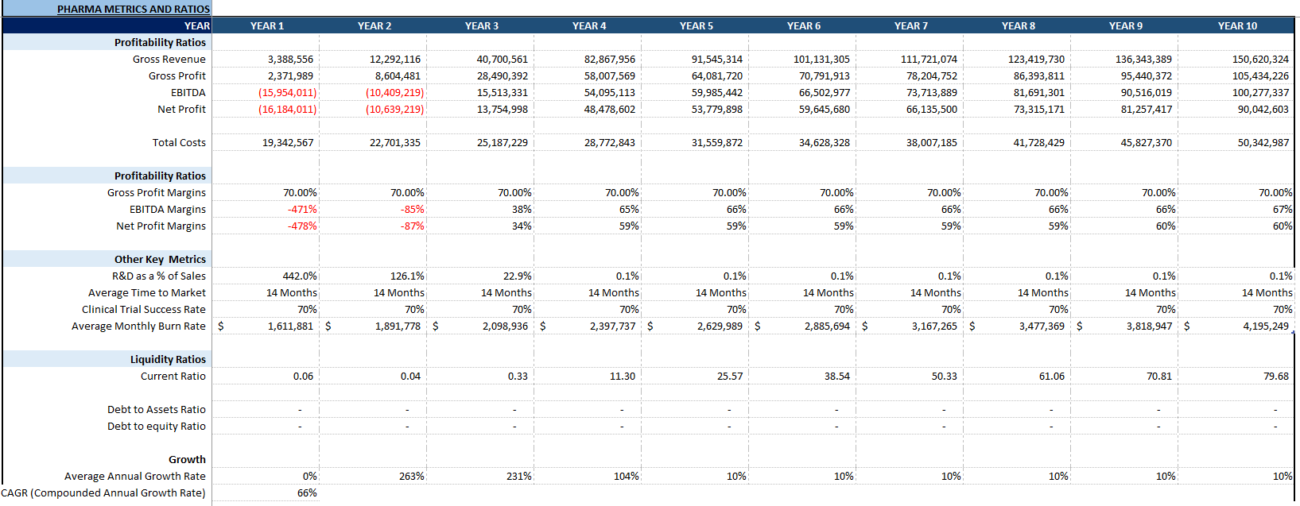
Financial Modeling Best Practices for Pharma and Biotech Companies
Financial modeling for pharma and biotech companies must reflect the unique dynamics of these industries. The following best practices can help ensure that financial models are both realistic and adaptable to uncertainty:
Account for Long Development Timelines
The development of a drug from the research phase to commercialization can take anywhere from 8 to 15 years, with substantial upfront investments required before seeing any returns. Financial models should account for these long timelines, including:
- Delayed Revenue Recognition: Revenue will not materialize until regulatory approval is achieved and a product is commercialized. Financial models should reflect the extended period before a drug can generate revenue, while considering factors like market penetration, pricing strategies, and competition.
- Stage-Gated Costs: In the R&D phase, costs are incurred in stages, such as preclinical trials, clinical trials (Phase I, II, and III), and regulatory submission. Each stage has its associated costs, with certain phases often requiring substantial investment. Financial models should reflect these stage-gated costs, as explored in depth by ScienceDirect.
- Capital Investment and Runway: Because of the long R&D timeline, financial models should account for the capital required to fund operations over several years. Companies should project their cash runway, determining how long they can continue operations before requiring additional funding.
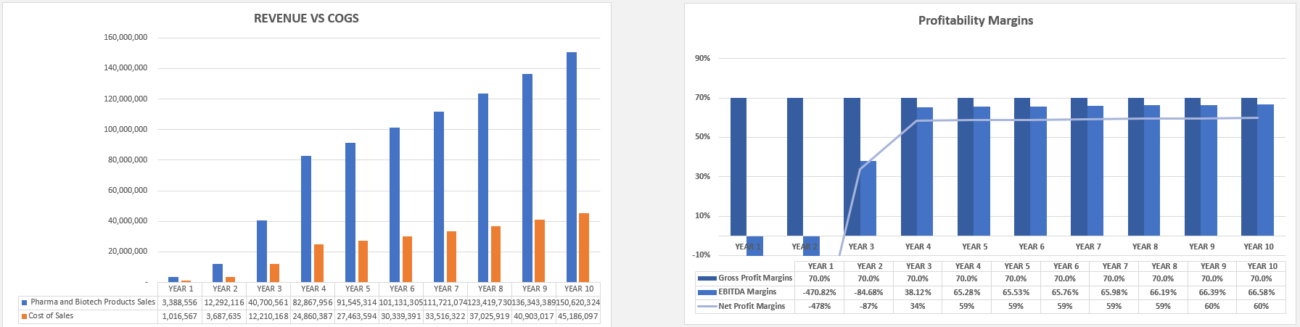
Scenario and Sensitivity Analysis
Given the high level of uncertainty, it’s important to incorporate scenario and sensitivity analysis into financial models. These tools allow companies to assess the impact of different assumptions and variables on financial outcomes. Check out how sensitivity analysis enhances scenarios on LinkedIn.
Cost Structure Modeling
Pharma and biotech companies typically have a high fixed cost structure, especially during the R&D phase, where the majority of expenses are related to salaries, clinical trials, and regulatory fees. However, variable costs, such as marketing expenses and cost of goods sold (COGS), increase as the company moves closer to commercialization.
Adjusting for External Risks and Uncertainty
External risks—such as changes in the regulatory environment, healthcare policies, or global economic conditions—can significantly affect a company’s financial performance. For insights on risk mitigation, consider the strategies discussed by FTI Consulting.

Continuous Monitoring and Model Refinement
Given the rapidly changing landscape in pharma and biotech, financial models should be viewed as dynamic tools rather than static documents. Continuous monitoring and refinement are essential to keep the model aligned with actual performance. Regular updates to assumptions, inputs, and projections based on real-world data help ensure that the financial model remains relevant and actionable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key risks in pharmaceutical financial modeling?
The key risks include R&D risk, regulatory risk, market and commercialization risk, operational and supply chain risk, and IP risk.
How does scenario analysis help in pharma financial modeling?
Scenario analysis helps companies create various potential outcomes and prepare for different market conditions, allowing them to strategize more effectively.
Why is sensitivity analysis important in pharma and biotech?
Sensitivity analysis evaluates how changes in specific inputs can impact financial outcomes, helping companies understand risk and adjust strategies accordingly.
By leveraging these financial modeling strategies, pharma and biotech companies can position themselves for success in a volatile industry, turning risks into opportunities and ensuring they remain leaders in innovation while maintaining financial health.



