The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries bring unique opportunities for high returns and considerable risks. Traditional valuation methods often fall short due to the uncertainties of drug development, regulatory hurdles, and extended timelines before profitability. Accurately valuing firms is vital for attracting investors, securing funding, and ensuring long-term sustainability. We have also built a ready-to-go Pharma and Biotech Valuation and Financial Model Template for Founders looking for an easy-to-use Financial model which will allow them to model out their businesses financials and provide an Income Statement, Balance Sheet and Cash Flow Statement for their business.

Why Valuation Matters in Pharma and Biotech Firms
Valuation is a critical component in financial modeling for pharma and biotech sectors. It affects investor interest and funding, dependent on the company’s potential for growth and profitability. Companies must achieve significant capital investment for drug development and clinical trials, which may take years to materialize market gains. Understanding financial health, development pipeline risks, and expected cash flows is crucial. Thus, valuation methods like these identify a company’s worth based on its present position and growth prospects.
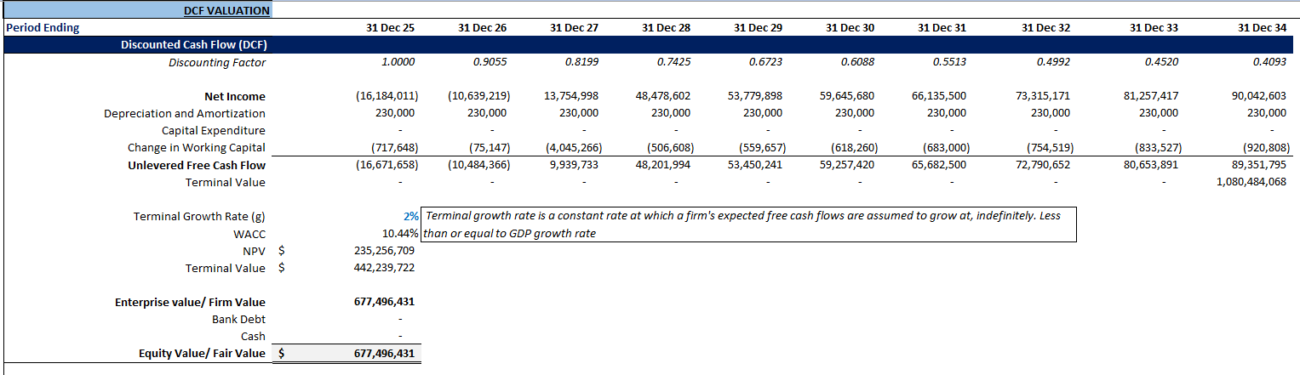
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
How DCF Works in Pharma and Biotech Valuation
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis is extensively used in valuing pharma and biotech firms, especially those nearing product launches. This involves calculating the present value of future cash flows using a discount rate. These cash flows are usually from drugs or therapies under development, but include uncertainties from long timelines and early-stage developments.
- Forecast revenue: Estimating revenue from drug sales, direct sales, royalties, and licensing.
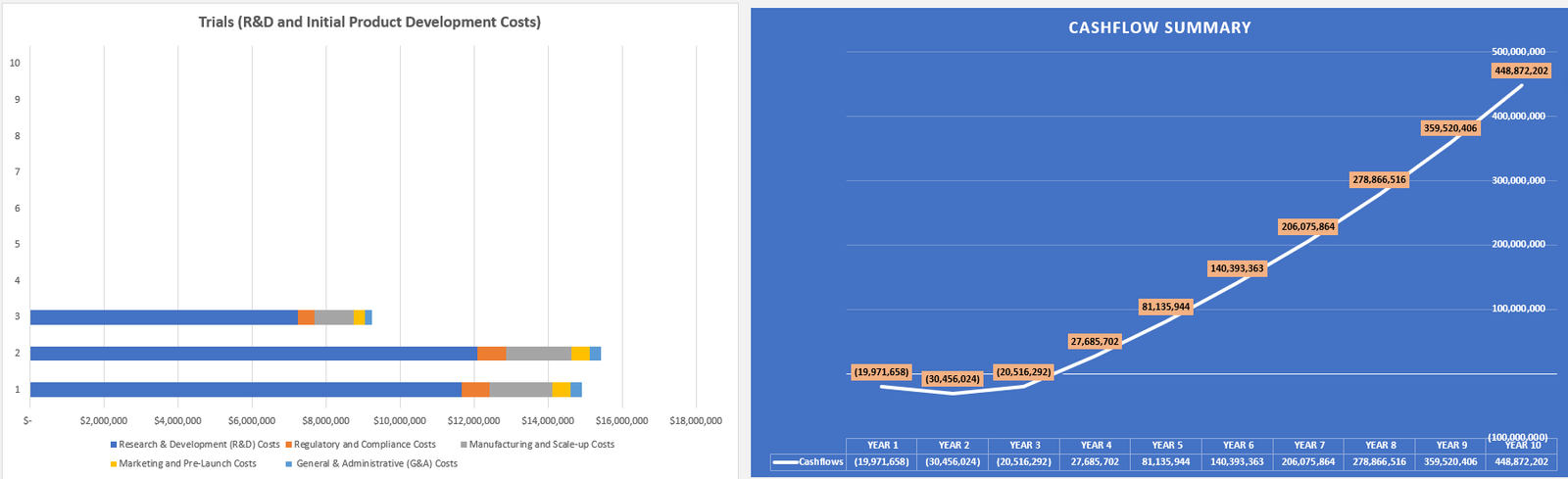
- Model costs: Accounting for substantial R&D, trial, manufacturing, and distribution costs.
- Risk adjustment: Applying a discount rate to reflect success probabilities in clinical trials and approval.
For instance, a company developing a cancer drug would need to include clinical trial costs, success rates, and market penetration expectations. Ultimately, DCF models factor in revenue projections discounted for risk.
Advantages and Challenges of DCF
- Advantages:
- Reflects long-term potential for financial stability.
- Offers clear insights into future cash flows for near-term product firms.
- Challenges:
- Navigating uncertainties in drug trial success.
- Managing long timelines (usually 5–10 years) to revenue generation.
Risk-Adjusted Net Present Value (rNPV)
Risk-Adjusted Net Present Value (rNPV) is pivotal in accounting for uncertainties and risk in drug development, improving over traditional NPV by integrating probabilities of success for each development stage. This approach is detailed further here.
How rNPV Works
- Forecast revenues: Project potential sales when drugs hit the market.
- Estimate costs: Include development, trial, regulatory, and manufacturing costs.
- Assign success probabilities: Allocate probability rates for each trial phase based on industry benchmarks.
- Discount cash flows: Use applicable rates reflecting time value and risks.
Advantages and Challenges of rNPV
- Advantages:
- Includes risk considerations for high-risk sectors.
- Useful for companies assessing multiple pipeline assets.
- Challenges:
- Dependence on quality data for accuracy.
- Requires deep insight into development processes and industry benchmarks.
Comparable Company Analysis (Comps)
Comparable Company Analysis is prevalent for valuing pharma and biotech firms with developed products. This method involves comparison to publicly traded industry peers.
How Comps Work
Analysts utilize financial metrics such as P/E ratio and EV/EBITDA to evaluate similar companies, focusing on firms in similar development stages.
Advantages and Challenges of Comps
- Advantages:
- Driven by market trends and reflects valuation benchmarks.
- Simplified and quick to apply compared to other methods.
- Challenges:
- Identifying truly comparable firms can be challenging.
- Doesn’t adjust for unique developmental risks.
Precedent Transactions Analysis (M&A Comps)
Precedent Transactions Analysis evaluates a firm’s value by examining similar sector acquisitions, offering insights from recent buyouts.
Advantages and Challenges of Precedent Transactions
- Advantages:
- Provides market-driven valuations.
- Beneficial for M&A consideration.
- Challenges:
- Valuations depend on evolving market conditions.
- Uniqueness of each deal may affect comparability.
Option Pricing Method (OPM)
The Option Pricing Method allows for sophisticated valuation models treating development stages as financial options. This method highlights the flexibility of strategies around drug portfolios.
Advantages and Challenges of OPM
- Advantages:
- Captures strategic development flexibilities.
- Effective for valuing multiple-asset companies.
- Challenges:
- Demands complex modeling and options theory comprehension.
- Relies heavily on market volatility and assumption accuracy.
Final Thoughts: Attracting Investors with a Solid Financial Model
Valuing pharmaceutical and biotech firms requires both nuanced strategy and sophisticated methods. Investors seek comprehensive models employing various methods like DCF, rNPV, and comparable analyses. To entice investors, companies must balance risk-reward, showcase growth potential, and accurately predict cash flows. Effective valuation underlines a firm’s potential and secures funding for bringing innovative solutions to market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Discounted Cash Flow method used for?
DCF is used to estimate the present value of future cash flows from drug commercialization, factoring in R&D and production costs.
How does the rNPV method differ from traditional NPV?
rNPV factors in success probabilities at each drug development stage, making it more suitable for high-risk biotech and pharma sectors.
Why use Comparable Company Analysis?
Comps provide a market-driven benchmark for valuation by comparing financial metrics of similar industry firms.



